
Precision Manufacturing from Design to Finish
The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining process is a highly accurate and efficient method for manufacturing complex parts and components. It begins with a digital design (CAD model), which is converted into machine instructions (G-code). The CNC machine then uses these instructions to control cutting tools, removing material from a workpiece with extreme precision. The process includes steps such as milling, turning, drilling, and finishing, ensuring each part meets exact specifications. With its ability to produce high-quality, repeatable results, CNC machining is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing across industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Our CNC Machining Process Workflow
The CNC machining process enables the efficient and precise manufacturing of complex parts through digital design, automated machining, and strict quality control. Its high precision, repeatability, and flexibility make it one of the core technologies in modern manufacturing.
Design and Programming
1.Create a 3D model of the part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
2.Convert the CAD model into a CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) program to generate G-code (machine instructions).
Material Preparation
1.Select the appropriate material (e.g., metal, plastic, or composite) based on part requirements.
2.Cut the material to a suitable size and secure it on the CNC machine’s worktable.
Machine Setup
1.Install the required tools (e.g., milling cutters, drills, lathe tools) and calibrate the machine.
2.Load the G-code program into the CNC machine’s control system.
Machining Process
1.The CNC machine automatically operates according to the G-code instructions, removing excess material through cutting, milling, drilling, and other operations.
2.During machining, the machine monitors tool position, speed, and cutting force in real time to ensure precision and quality.
Quality Inspection
1.Use measuring tools (e.g., calipers, micrometers, CMMs) to inspect the dimensions and shape of the machined part.
2.Ensure the part meets design requirements and tolerance standards.
Surface Treatment
Perform surface treatments such as polishing, sandblasting, plating, or coating as needed to enhance appearance and performance.
Assembly and Delivery
1.Assemble the finished parts (if required) and package them.
2.Deliver to the customer or proceed to the next production step.
Our technological advantages
1.CNC machines can achieve micron-level precision, ensuring each part meets strict design requirements.
2.Through digital control, CNC machining delivers highly consistent repeatability, making it ideal for mass production.

1.CNC machines can operate continuously 24/7, significantly improving production efficiency.
2.High automation reduces manual intervention, minimizes human error, and saves time and costs.

1.By changing tools and adjusting programs, CNC machines can produce parts with complex geometries, suitable for small-batch, multi-variety production.
2.Capable of machining various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, to meet the needs of different industries.

Our equipments
-1-scaled.avif)
-scaled.avif)
-scaled.avif)
-scaled.avif)
-scaled.avif)
-scaled.avif)
our team
Our craft team
The process technology team focuses on providing efficient technical support and solutions for industrial production. The core members are composed of experienced process technicians, who have profound attainments in the fields of casting, stamping, welding, painting, etc., and can quickly solve production problems. The team also includes young process engineers, who have innovative thinking and solid knowledge to inject vitality into the team. The team is equipped with advanced experimental equipment to ensure the optimization and improvement of the process flow. We are committed to promoting the continuous development and innovation of industrial production.

Our sales team
1. Team members
Our sales team consists of a group of experienced and dynamic members, each with a unique expertise in the field of sales.
2. professional ability
Team members have deep professional knowledge, can accurately grasp customer needs, to provide professional products and services.
3. Sales performance
The team has achieved remarkable sales performance, steadily increased its market share, and won wide recognition from customers.
4. Customer feedback
We value customer feedback, take customer needs as the orientation, and continuously improve service quality and customer satisfaction.
5. Spirit of cooperation
Team members work closely together to meet challenges and ensure successful sales targets.
6. Continuous innovation
The team continues to explore new sales strategies and technical means to maintain a leading position in the market.
Vii. Future Development
In the future, we will continue to strengthen team building, enhance professional capabilities, and provide customers with more excellent services.

Our management team
1. core members
Our management team consists of senior industry experts with extensive management experience and forward-looking strategic vision.
2. management style
We focus on people-oriented management, encourage teamwork, and work together to address challenges through open and transparent communication.
3. Decision-making ability
With data analysis and market research, we make quick decisions to ensure the company’s steady growth.
Fourth, strategic vision
We have insight into market trends, timely adjustment of strategy, and point out the direction for the development of the company.
5. Social Responsibility
We actively fulfill our social responsibility, pay attention to environmental protection, employee welfare, and commit to the sustainable development of the enterprise.
Sixth, look to the future
We will continue to improve management, innovate business models, and work with partners to create a better future.

Our after-sales service team
Our after-sales service team is focused on providing our customers with an exceptional service experience. Here are five highlights from the team:
Technical expertise: Our engineers are highly skilled, able to respond quickly and solve customers’ technical problems.
Comprehensive maintenance: Provide a full range of repair and maintenance services to ensure the normal operation of equipment.
Customer first: Always put customer satisfaction first, listen to needs, and actively improve.
Efficient resolution: Quickly locate problems and provide efficient solutions to reduce customer wait times.
Continuous improvement: Continuous learning and training to adapt to technological changes and improve service levels.


Aluminum Extrusion

Laser Cutting

Injection Molding
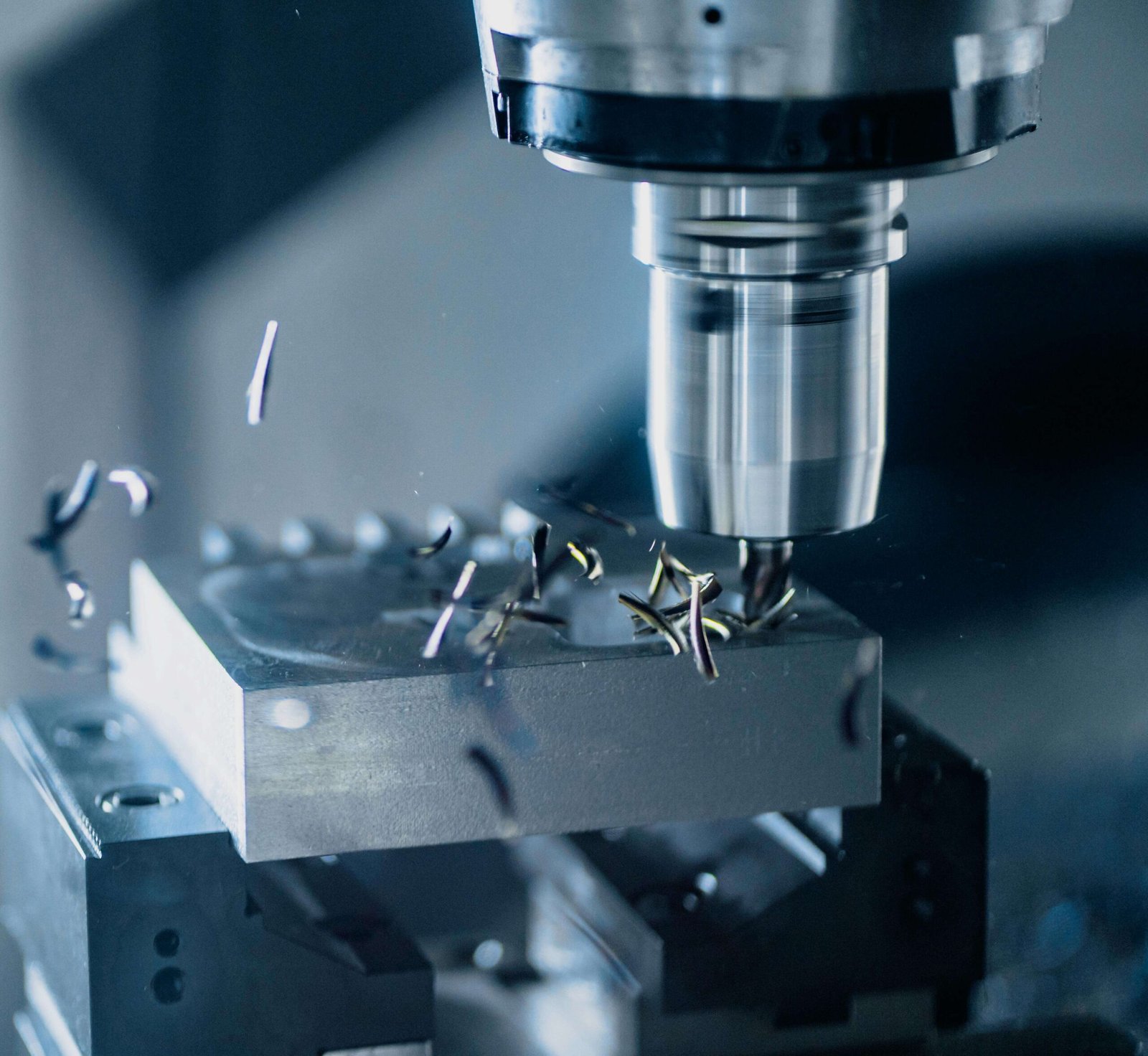

CNC Machine Tool Production

Metal Die Casting



























-scaled.avif)